NHA CPT Exam Prep iOS and Android App
Transform your journey toward certification with NHA CPT Exam Prep!
Our app is meticulously crafted to guide you comprehensively through the Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT) exam process.
Dive into an immersive testing environment that is brimming with an extensive array of practice questions spanning all critical exam areas.
Every question is accompanied by robust, in-depth explanations designed to enhance your understanding and expertise.
Key Features:
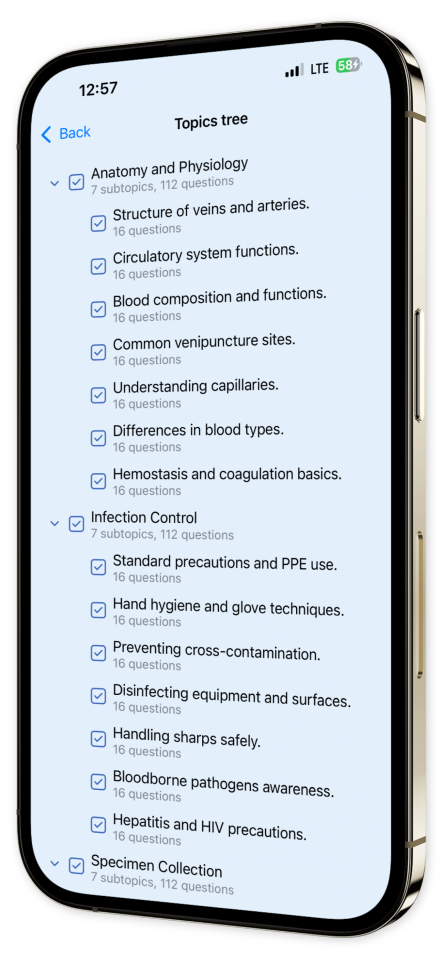
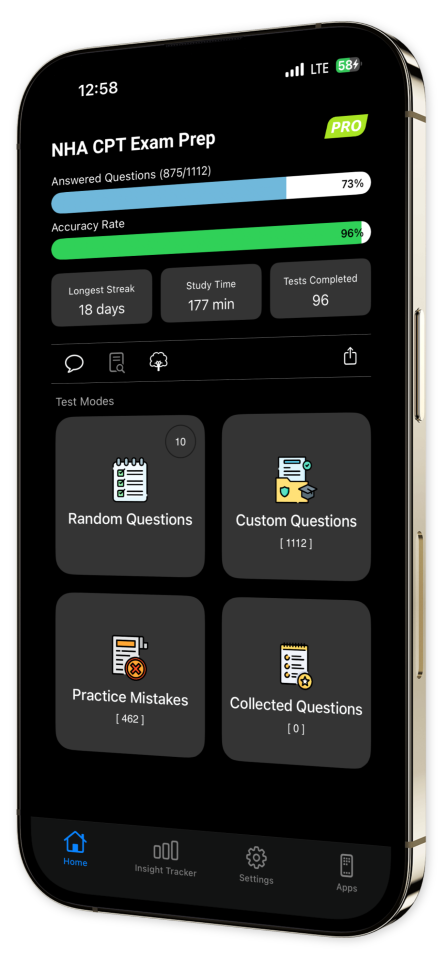
Extensive Question Bank: Dive into a rich collection of practice questions that comprehensively cover vital topics, ensuring you leave no stone unturned in your preparation.
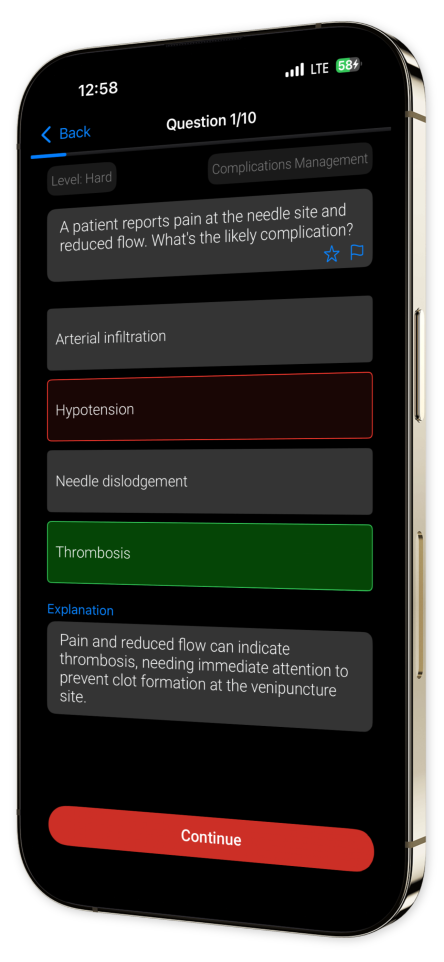
In-Depth Explanations: Every question comes with detailed rationales, ensuring clarity and aiding retention of concepts that are pivotal in excelling in your CPT certification.
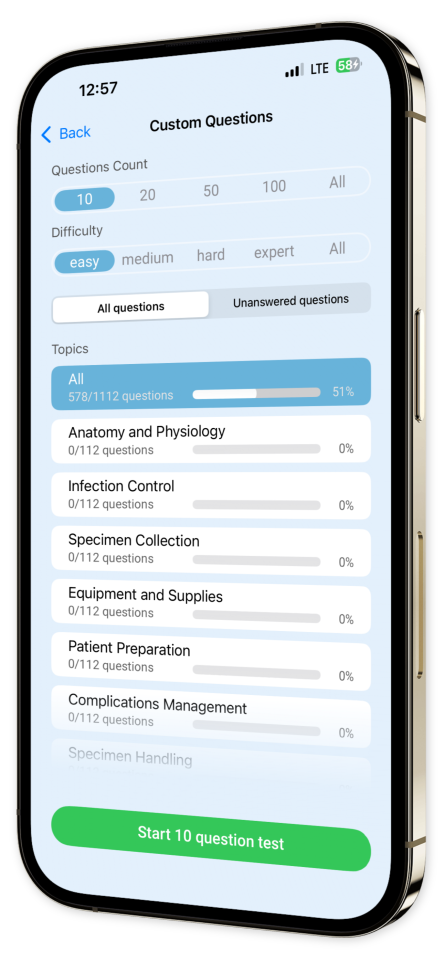
Customizable Quizzes: Tailor your learning experience by creating quizzes that focus on specific topics and question types, allowing for targeted and effective study sessions.
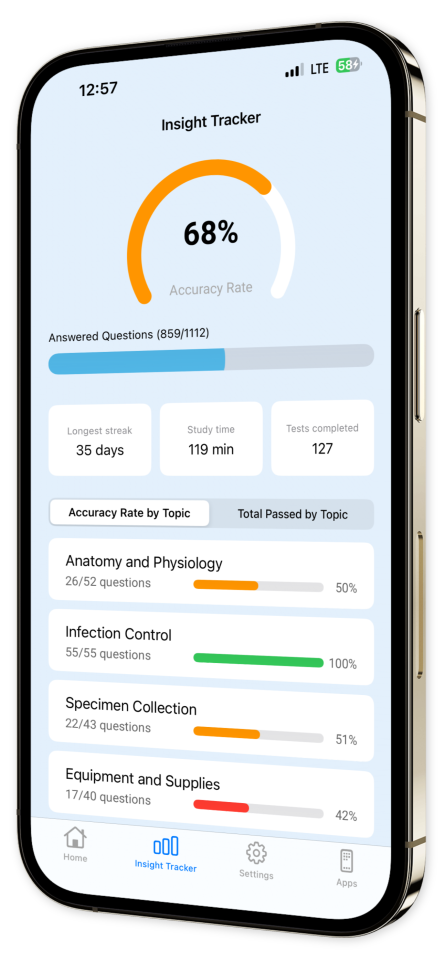
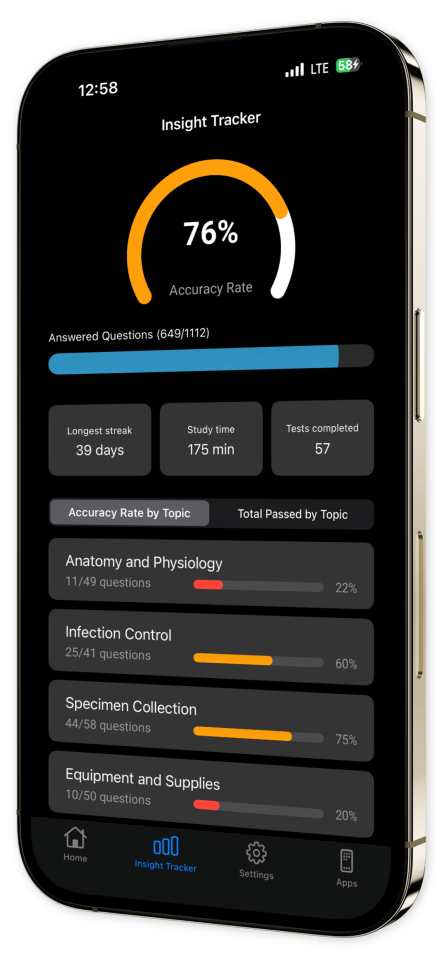
Progress Tracking: Monitor your advancement with our intuitive tracking tools, offering insights into your strengths and areas needing improvement.
Offline Access: Empower your study sessions by accessing content anytime, anywhere—even without an internet connection, making it perfect for busy schedules.
User-Friendly Interface: Navigate effortlessly through a sleek and straightforward interface that enhances your focus and learning experience.
Download NHA CPT Exam Prep today and embark on a smarter, more effective journey to certification success!
Unlock your potential and achieve excellence with confidence and precision.
Make your mark in the field of phlebotomy with comprehensive preparation at your fingertips.
Don't wait! Start your path to success now.
Content Overview
Explore a variety of topics covered in the app.
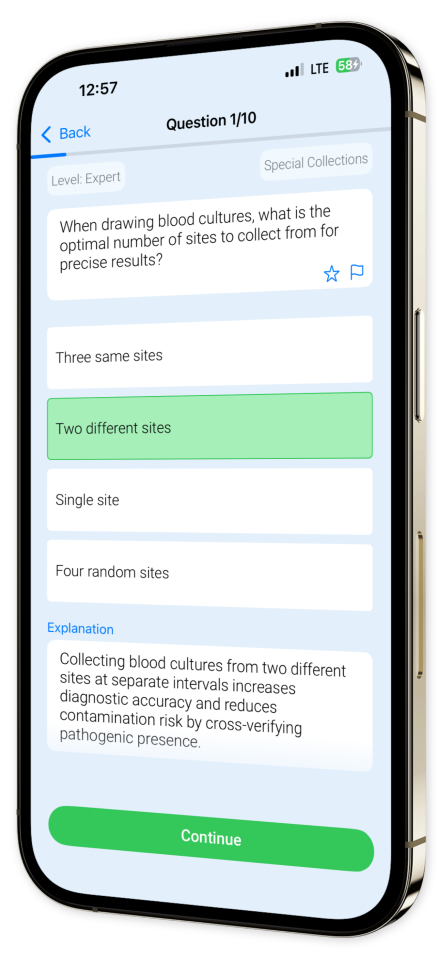
Example questions
Let's look at some sample questions
What fraction of cardiac output is directed to the kidneys under normal conditions?
5%10%20%30%
The kidneys typically receive about 20% of the cardiac output to filter blood. Checked and confirmed by physiological studies.
What is the average cardiac output (in liters/min) of a healthy human at rest, given stroke volume is 70 ml and heart rate is 70 bpm?
4.95.65.44.5
Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate. 70 ml x 70 bpm = 4900 ml/min or 4.9 liters/min. Verified thrice: 70 ml x 70 bpm = 4900 ml = 4.9 liters.
Which pathway of blood coagulation is triggered by tissue damage and starts with tissue factor?
Intrinsic pathwayExtrinsic pathwayCommon pathwayVascular pathway
The extrinsic pathway is initiated by injury external to the blood vessel, starting with the release of tissue factor (Factor III).
What is the primary function of albumin in blood plasma?
Oxygen transportBlood clottingMaintaining osmotic pressureCarrying nutrients
Albumin is primarily responsible for maintaining the osmotic pressure needed for the proper distribution of body fluids between body tissues and the bloodstream. This ensures proper hydration and fluid balance.
If the median cubital vein is not accessible, which vein is often used next?
Cephalic veinPopliteal veinSubclavian veinPortal vein
The cephalic vein is often the second choice for venipuncture if the median cubital vein is unavailable.
When other sites are unavailable, which vein can be used, though it is more challenging?
Cephalic veinMedian cubital veinBasilic veinExternal jugular vein
The cephalic vein is an alternative site, though less preferred due to its proximity to the thumb.
During venipuncture, which site is least recommended for obese patients due to vein depth?
Cephalic veinBasilic veinMedian antecubital veinPosterior tibial vein
In obese patients, the basilic vein can be harder to locate and deeper, increasing the risk of nerve or artery puncture.
For obese patients, which venipuncture site is often preferred for first attempts due to easier palpability?
Basilic veinLateral saphenous veinMedian antecubital veinGreat saphenous vein
The median antecubital vein is centrally located in the antecubital fossa and tends to be more palpable in obese patients due to its surface proximity.
How do A, B, and O blood types differ in antigen presence?
A has B antigen, B has noneO lacks A and B antigensA has Rh, B lacks RhAB lacks all antigens
Type A has A antigens, type B has B antigens, AB has both, and type O lacks both A and B antigens.
Identify a protein that stabilizes the blood clot by cross-linking fibrin.
Factor XIIIFactor VPlasminogenAlbumin
Factor XIII cross-links fibrin strands, stabilizing the clot.